Protein Activity Assay
Overview
Teaching: 30 min
Exercises: 240 minQuestions
What molecules can act as substrates for our protein of interest?
Objectives
Students will understand that enzymes catalyze reactions in which substrates are converted to products.
Students will know that enzymes have optima, or favored conditions, that should be considered in an assay.
Students will know that specific activity can indicate an enzyme preparation’s general “quality”.
Students will know the basic premise of the p-nitrophenylacetate assay for hydrolases.
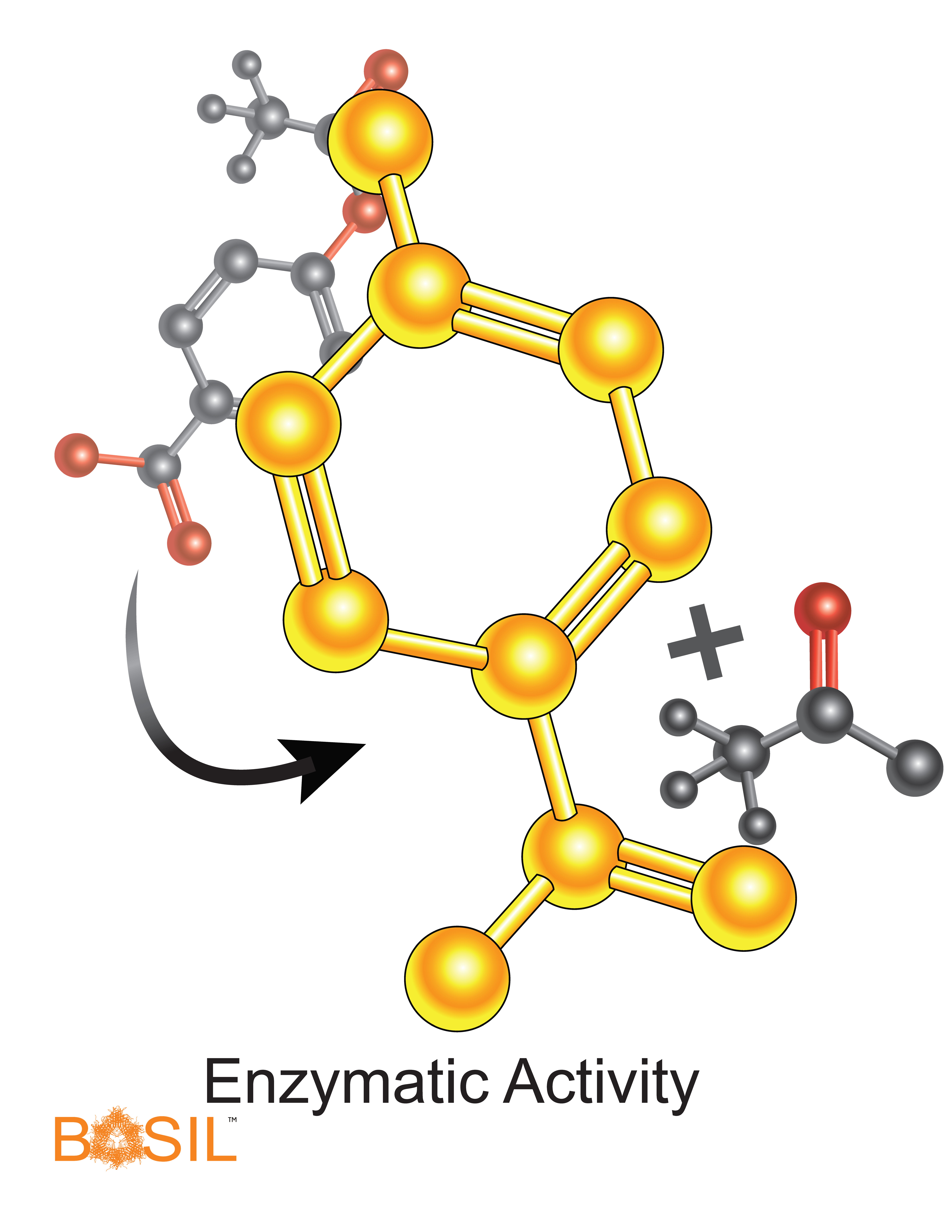 The conformation of an enzymatic product confirms the function of an enzyme. Many hydrolases will hydrolyse p-nitrophenyl acetate (PNPA), acetate and p-nitrophenol (PNP) producing a yellow color. This module focuses on confirming the hydrolysis function of the protein previously purified. In addition, substrates identified as part of the bioinformatics experiments can be tested to confirm or deny their identify as substrates for the protein of interest.
The conformation of an enzymatic product confirms the function of an enzyme. Many hydrolases will hydrolyse p-nitrophenyl acetate (PNPA), acetate and p-nitrophenol (PNP) producing a yellow color. This module focuses on confirming the hydrolysis function of the protein previously purified. In addition, substrates identified as part of the bioinformatics experiments can be tested to confirm or deny their identify as substrates for the protein of interest.
Module Resources
Key Points
Activity assays with a broad substrate can be used to identify the class of enzyme while specific substrates can yield more information about enzyme function.