Protein Purification
Overview
Teaching: 45 min
Exercises: 300 minQuestions
How can an expressed protein be purified from a bacterial cell preparation?
Objectives
Students will compare the use of sonication vs enzymes vs other disruption techniques for cell wall breakage.
Students will describe how the choice of buffer (and other buffer ingredients and additives) can protect or damage an enzyme’s structure and function.
Students will describe why protein samples should be kept on ice at all times.
Students will give a justification for the statement that proteins should be studied in purified form rather than in the ligand-bound or complexed forms they may take up in the cell.
Students will describe methods for the removal of nucleic acids and extraneous membranes and lipids.
Students will describe how to read a plasmid vector map to ascertain whether a tag will be expressed.
Students will describe how a protein tag can allow one-step isolation of a foreign protein from E. coli but may require tag removal after purification.
Students will describe how to bind and elute a recombinant protein from the appropriate affinity resin.
Students will describe treatments that may be necessary after chromatography, such as elution agent removal or protein concentration.
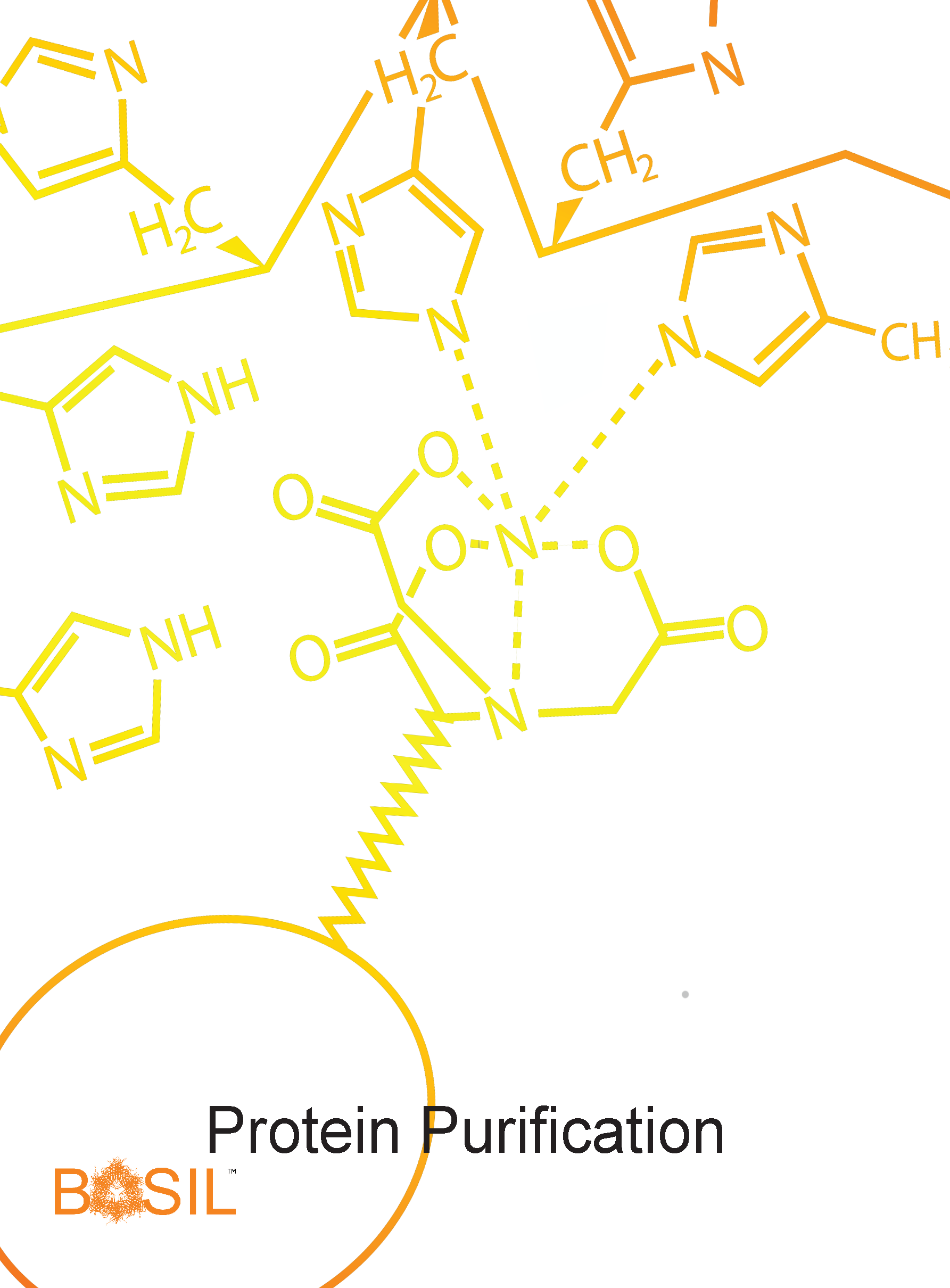 Protein purification is used to isolate a protein of interest from all other cellular components. In this study, purification includes extracting all proteins from a cell pellet, removing debris such as cell membranes and nucleic acids, and performing appropriate affinity chromatography, which is possible because the protein of interest has a tag for the purpose. Techniques for this exercise include sonication, centrifugation, and chromatography. Students will assess the purity of the protein in a subsequent experiment with SDS-PAGE. If purification was not successful, students will have to identify potential reasons why and test their hypothesis by repeating purification. The correct protein must be properly tracked throughout the procedure as it is not visible to the human eye. Protein purification is dependent on the successful completion of protein expression and likewise, the only way to determine if protein purification was successful is by completion of all subsequent labs.
Protein purification is used to isolate a protein of interest from all other cellular components. In this study, purification includes extracting all proteins from a cell pellet, removing debris such as cell membranes and nucleic acids, and performing appropriate affinity chromatography, which is possible because the protein of interest has a tag for the purpose. Techniques for this exercise include sonication, centrifugation, and chromatography. Students will assess the purity of the protein in a subsequent experiment with SDS-PAGE. If purification was not successful, students will have to identify potential reasons why and test their hypothesis by repeating purification. The correct protein must be properly tracked throughout the procedure as it is not visible to the human eye. Protein purification is dependent on the successful completion of protein expression and likewise, the only way to determine if protein purification was successful is by completion of all subsequent labs.
Module Resources
Key Points
Purification of proteins is usually accomplished by lysis, removal of nucleic acids, and affinity chromatography utilizing a 6-histidine tag or fusion protein tag.